What is AnMBR?
AnMBR (Anaerobic Membrane Bioreactor) is an advanced biological treatment system that combines anaerobic digestion with membrane filtration. It enables high-strength wastewater treatment, organic matter removal, and biogas generation in a compact and closed system.
Key Features
- High organic load tolerance
- Zero sludge discharge potential
- Energy recovery through methane-rich biogas
- Low excess sludge production
- Excellent effluent quality due to membrane filtration
How AnMBR Works
AnMBRs utilize anaerobic microorganisms in a bioreactor to degrade organic pollutants in the absence of oxygen. Membranes (either external or submerged) retain biomass and solids, allowing only treated water to pass through. Biogas produced in the process can be captured and used as renewable energy.
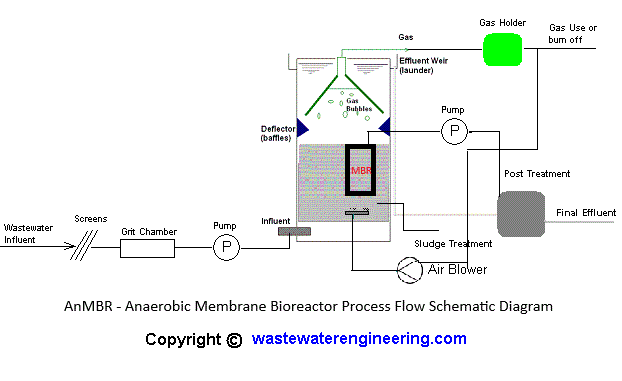
Process Flow Diagram of AnMBR
The diagram below outlines a typical AnMBR configuration, showing influent pretreatment, anaerobic bioreactor, membrane filtration, and biogas utilization stages.
Applications
AnMBR is ideal for treating high-strength industrial wastewaters such as from food and beverage, pulp and paper, and chemical industries. It is also suitable for municipal wastewater with energy recovery needs.
Advantages Over Conventional Anaerobic Systems
- Higher effluent quality
- Stable operation under variable loads
- Complete biomass retention
- Compact system layout
- Renewable energy production
Disadvantages of AnMBR
- Water quality may still not be good enough due to limitation of Anaerobic process itself
- Aeration arrangement using the produced methane is not easy to implement
